Choose the content to read
- What disease does knee replacement treat?
- How many types of knee replacements?
- What is the total knee replacement procedure?
- What is the recovery time for knee replacement?
- What is the success rate of knee replacement?
- ROSA: Robotic Assisted Knee Replacement
Knee replacement
Knee replacement, or knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure for treating severe osteoarthritis with total or partial knee replacement to reduce joint pain, stiffness, bowleg, and deformities due to age-related degenerative knee joints, obesity, or knee joint injury. Knee replacements significantly improve knee strength and efficiency. Currently, knee replacement has made significant progress with robotic-assisted knee replacement, aiding in the accurate positioning of prosthetic knee joints, precise joint alignment, and balanced ligaments, resulting in minimal tissue injury, less blood loss, and fast recovery, enabling quick full-functioning knee joints, whether steps, walks, standing, getting up, or sitting down, and allowing patients to perform various daily activities safely.
Why knee replacement?
Severe osteoarthritis results in degeneration, erosion, and thinning of articular cartilage that supports and cushions between the lower end of the femur and the upper end of the tibia. Osteoarthritis leads to joint space narrowing, frequent friction between knee joint surfaces, and inflammation of joints and surrounding tissues (synovial membrane). As a result, the knee joint exudes excess water into the joint (knee effusion), which causes stretched ligaments, a loose knee joint, a swollen knee, and synovitis, resulting in joint pain, joint stiffness while walking, a locked knee, joint stiffness, knee noise (crepitus), and weakened periarticular muscles causing unsteady gait, making walking and bodily movement difficult.
Knee replacement surgery is the most efficacious treatment option for severe osteoarthritis, which cannot be treated with other medical treatments. Knee arthroplasty helps reduce knee pain, locked knee, joint stiffness, and knee noise; eliminates osteoarthritis and corrects knee deformity; increases the strength of the knee joint and periarticular muscles; improves knee mobility efficacy; and allows you to walk with full weight bearing on the operated leg.
What disease does knee replacement treat?
- Knee osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout and pseudogout
- Post-traumatic arthritis
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
- Knee pain, dull pain around the joint.
- Joint stiffness, a locked knee
- Swollen knee, bowleg, and knee deformity.
- Knee noise when moving the body.
- Difficulty in knee straightening and bending
- Difficulty in walking, standing, and sitting
- Knee muscle atrophy
- Chronic knee aches, even when lying down or sitting still
(Left) Total Knee Replacement (Right) Severe Osteoarthritis
What is the diagnosis of osteoarthritis?
Orthopedic surgeons will diagnose osteoarthritis by inquiring about knee pain history, including the nature of the pain, whether it worsens with movement or activity, and its severity. Inquire whether the patient has any previous treatment or medication, when the pain occurs, and the use of walking aids, followed by conducting physical examination and radiographic imaging as follows.
- Physical examination: Inspect the knee joint appearance to determine whether it is normal. Assess knee conditions, including walking posture and weight bearing while walking. Look for signs of bowleg, twisted knee, or deformed knee by palpating the knee joint for signs of swelling, warm knee, hot knee, or localized knee pain. Examine joint range of motion, joint stiffness, locked knee, and joint mobility by bending and stretching to determine the degree of stiffness, etc.
- X-rays examine knee joint structures, bone alignment, and the width of the joint space to determine the extent of articular cartilage degeneration.
- MRI: A 3D imaging to examine the entire knee bony structure and articular cartilage in cases where there is a suspicion of associated soft tissue injury, such as a torn ligament or meniscus, or in cases where the symptoms of the disease do not correspond to the X-ray images.
How many types of knee replacements?
There are 2 main types of knee replacements that are regarded for achieving optimal outcomes as follows:
- Unicompartment knee arthroplasty (UKA), or partial knee replacement, is a surgery to replace inner-side osteoarthritis by removing a portion of the deteriorated articular cartilage while leaving the healthy outer articular cartilage intact. UKA helps preserve healthy knee joint components, such as cartilage, the anterior cruciate ligament, and surrounding tissues, allowing patients to recover much faster.
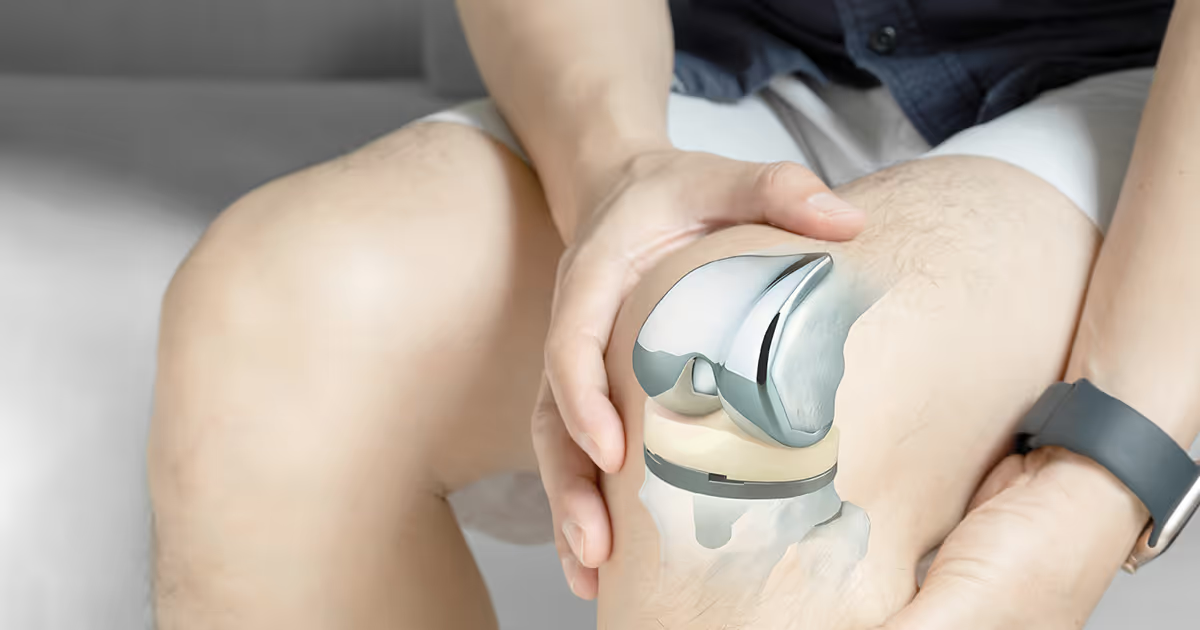
- Total knee replacement is surgery to replace all parts of the articular cartilage to treat severe osteoarthritis with total articular cartilage erosion, frequent friction of joint surfaces, bowlegs, deformed joints, bone spurs surrounding the knee joint, and difficulty moving due to stiff joints. The orthopedic surgeon will consider total knee replacement with a prosthetic joint to replace the damaged components, including the femur, the tibial ends, and possibly the patella, to relieve pain, enabling the patient to resume a steady knee joint functioning
What is the total knee replacement procedure?
Total knee replacement procedure at MedPark Hospital adopts the gold standard in surgery, prioritizing safety and treatment success outcomes to achieve the treatment goal of relieving knee pain, increasing knee joint function, and enhancing physical mobility to allow patients to resume their daily activities quickly.
Preparation for knee replacement
- The orthopedist will advise you to do ankle pumping exercises before surgery to increase blood circulation and prevent the risk of complications.
- Stop or quit smoking, eat the 5 food groups, and drink plenty of water to avoid irregular bowel movements.
- 7 days before surgery, stop taking antiplatelets such as aspirin, clopidogrel, or warfarin, as well as some vitamins and supplements. Those taking underlying medications or having a history of drug allergies must inform the orthopedist in advance.
Total knee replacement procedure
- The anesthetist will perform a spinal block and administer general anesthesia to put the patient to sleep. The orthopedic surgeon will then perform a total knee replacement by making a single incision to remove all deteriorated articular cartilage and lesions at the lower end of the femur, the head of the tibia, and the patella.
- If a bone spur is present, the orthopedic surgeon will cut and remove it altogether with deteriorated cartilage, followed by removing the joint surfaces by making bone cuts at the level to ensure proper fit with the implant components.
- The orthopedic surgeon will adjust the balance of ligamentous tension and laxity and connective tissues to create appropriate space before inserting the implant knee joints while checking the knee joint alignment using bone reference landmarks obtained from preoperative x-ray imaging.
- The orthopedic surgeon will insert a femoral implant at the lower end of the femur and a tibial implant at the head of the tibia, padded with a plastic spacer between the two knee joints to replace the deteriorated articular cartilage. Once the implants are securely in place, the orthopedic surgeon will evaluate the range of knee extension and flexion to ensure optimal mobility before stitching the wound. The surgery takes approximately 2 hours.
Post knee replacement
- The orthopedist will have you wear compression stockings to reduce the risk of blood clots, as well as cold compresses to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- The orthopedist will have you lie supine and put a pillow slightly below the knee joint to allow you to fully extend your knee. If you feel aches, you can switch to putting a pillow under your knee.
- The orthopedist will have you begin physical therapy within 24 hours, alternating between full knee flexion and extension every day.
- The orthopedist will instruct you on how to practice walking with a walker, transitioning from sitting to standing, and climbing and descending stairs.
What are postoperative knee replacement precautions?
- Take painkillers continuously as prescribed by the orthopedist. If you experience severe pain, the wound is hot, or you have redness or a fever, seek medical attention right away.
- Be careful not to fall, stumble, or slip when walking in a wet bathroom, on slippery floors, or stepping. Install handrails in the bathrooms.
- Be careful not to twist your knees while walking. Note that the tip of your big toe should not be tilted inward or outward when placing your feet and walking.
- Do not sit for longer than 45-60 minutes and avoid lifting heavy objects.
What is the recovery time for knee replacement?
Typically, patients undergoing total knee replacement gradually recover after surgery. They can walk without a walking device for 3 weeks, drive in 4-6 weeks, and fully recover in 2-3 months, depending on age, physical strength, and preoperative knee-strengthening exercises as advised by the orthopedic.
What are the complications of knee replacement?
Common complications from knee replacement include knee infection, deep vein thrombosis, fracture of the artificial knee, blood vessel, or nerve damage. However, the incidence of these complications is very low, at less than 5%. Typically, knee replacement, or knee arthroplasty, is generally regarded as a highly effective and safe surgery.
What is the success rate of knee replacement?
Knee replacement is regarded worldwide as an effective treatment method for treating severe osteoarthritis, offering optimum treatment outcomes. According to a survey of patients who have undergone knee replacement surgery, more than 90% can function well 15 years after the surgery, while 82% can still function with their knee normally 25 years after the surgery.
What are the benefits of knee replacement?
- Relieve knee pain: Knee replacement significantly reduces and relieves knee pain. After the surgery, some patients can have a full recovery from knee pain.
- Improved mobility: Knee arthroplasty enables you to get up, sit, stand, walk, move your body, and participate in physical activities like walking, swimming, golfing, or cycling.
- Improved daily routine: Knee arthroplasty allows you to participate in a variety of daily activities more easily. Reduces staying still and dependence, allowing you to walk up and down stairs, get in and out of cars, and help yourself more effectively.
- Correct knee deformities: Knee replacement can correct bowlegs, deformities, and the inability to fully extend and flex the knee by providing strong, stable, and fully functional knees.
- Improved quality of life: Knee replacement significantly improves quality of life, giving you back your “life,” and allows you to go out with friends, go sightseeing, and engage in activities you used to love.
Knee replacement at MedPark Hospital
Orthopedic Center, MedPark Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand, led by a team of orthopedic surgeons with extensive experience both nationally and internationally, is ready to provide seamless diagnostic and intervention for treating complex osteoarthritis at all ages, using state-of-the-art medical technology and FDA-approved clinical equipment and JCI standard operating theater, combined with advanced surgical techniques, aids in treatment accuracy, safety, and efficiency while providing postoperative care and evaluation to reduce complications, enables patients to move their bodies with confidence, have strong physical health, and have a better quality of life in a long run, and can perform daily activities fully.
ROSA: Robotic Assisted Knee Replacement
MedPark Hospital adopts ROSA robotic-assisted surgery technology equipped with 3D X-ray imaging as an alternative surgery option to partial or total knee replacement to treat severe osteoarthritis, which helps increase the precision of each anatomical parameter specification to aid patients undergoing the surgery in regaining their knee joints functioning, including walking, standing, and sitting, and engaging in various activities in daily life efficiently. The highlights of the ROSA robotic-assisted surgery include:
- Notably precise positioning of the implant knee joints
- Greatly balance the knee joint alignment and ligament tension
- Markedly minimizes muscle and surrounding tissue injuries
- Significantly reduce surgical wound size and minimize blood loss
- Remarkably alleviates postoperative pain and aids in a quick recovery
Related Article
- Knee replacement surgery journey to regain strong steps and pain-free movement
- Is walking possible a few days after total knee replacement?
Related Package